Aloe vera is one of those plants that seems to have everything going for it. It's not just a pretty face with its striking, succulent leaves; it's a plant that's been valued for centuries for its medicinal and cosmetic uses. But what exactly is an aloe vera plant, and why does it deserve a spot in your home?
In this article, we'll explore all things aloe vera. We'll look at its characteristics, its rich history, and how you can care for it in your own space. Whether you're a seasoned plant parent or just starting your green journey, you'll find plenty of useful insights to help you understand and care for this fascinating plant.
What Is Aloe Vera?
Aloe vera, scientifically known as Aloe barbadensis miller, is a succulent plant species that belongs to the Aloe genus. It's native to the Arabian Peninsula but has been cultivated around the world for its attractive appearance and myriad uses. The plant typically grows in warm and dry climates, making it a hardy addition to your plant collection.
The aloe vera plant is easily recognizable by its fleshy, greenish leaves that fan out from a central base. These leaves are often adorned with small white specks and have serrated edges. Not only do these leaves look cool, but they're also where the magic happens. Inside, they contain a gel-like substance that has been used for centuries in traditional medicine and skincare.
But why is aloe vera so popular? Beyond its aesthetic appeal, it's known for its soothing properties. Many people reach for aloe vera gel to treat minor burns, sunburns, or skin irritations. It's a true multitasker, offering both beauty and utility. Aloe vera can be a real conversation starter, as it bridges the gap between ornamental and practical plants.
The History of Aloe Vera
Aloe vera has a fascinating history that spans thousands of years. Ancient Egyptians referred to it as the "plant of immortality," and it's said that even Cleopatra used it as part of her beauty regimen. The plant has also been mentioned in ancient texts from Greece, Persia, and Rome, highlighting its longstanding significance across cultures.
In traditional Chinese and Indian medicine, aloe vera was valued for its healing properties. It was often used to treat skin conditions, digestive issues, and inflammation. The plant's gel was considered a valuable commodity, and its cultivation spread throughout Africa, Asia, and eventually to the New World.
Fast forward to the present day, and aloe vera is still cherished for its versatility. From skincare products to health supplements, its uses have expanded even further. It's not just a plant; it's a testament to the enduring relationship between humans and nature. As you bring an aloe vera plant into your home, you're connecting with a rich history of botanical appreciation.
How to Care for Your Aloe Vera Plant
Caring for an aloe vera plant is easier than you might think. These resilient succulents are low-maintenance, making them perfect for beginners and busy plant lovers. Here are some tips to keep your aloe vera thriving:
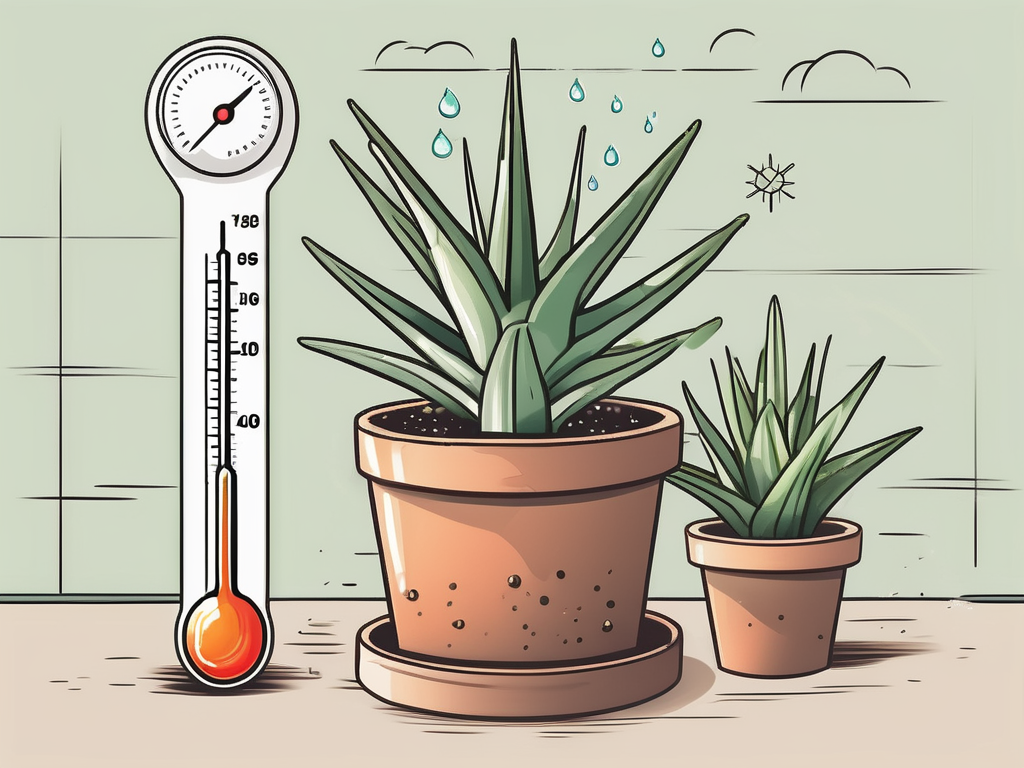
- Light: Aloe vera loves bright, indirect sunlight. Place it near a sunny window, but avoid direct sun, which can scorch the leaves.
- Watering: Allow the soil to dry out completely between waterings. Overwatering is a common mistake and can lead to root rot. Water sparingly, especially in the winter months.
- Soil: Use a well-draining potting mix designed for succulents and cacti. This will help prevent waterlogged roots.
- Temperature: Aloe vera prefers temperatures between 60-75°F (15-24°C). Keep it away from drafty windows in the winter.
- Fertilizing: Feed your aloe vera plant with a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer diluted to half strength during the growing season (spring and summer).
By following these simple guidelines, you'll find that your aloe vera plant is a forgiving and rewarding companion. It's all about finding the right balance and understanding its needs.
Common Problems and Solutions
Even though aloe vera is a hardy plant, it can still face a few challenges. But don't worry, many of these issues are easy to fix once you know what to look for.
Overwatering: This is the most common problem with aloe vera plants. If you notice the leaves turning brown or mushy, it's likely due to overwatering. Let the soil dry out completely before watering again, and ensure your pot has proper drainage.
Underwatering: On the flip side, underwatering can cause the leaves to become thin and shriveled. If this happens, give your plant a good drink and monitor the soil moisture going forward.
Pests: Aloe vera is generally pest-resistant, but occasionally, you might spot aphids or mealybugs. Use a gentle insecticidal soap or neem oil to treat infestations.
Sunburn: If you notice brown spots on the leaves, your aloe vera might be getting too much direct sunlight. Move it to a spot with more indirect light to prevent further damage.
By keeping an eye out for these common issues, you can ensure your aloe vera remains healthy and vibrant. Remember, every plant has its quirks, and learning how to care for them is part of the fun!
Propagating Aloe Vera
One of the joys of owning an aloe vera plant is that you can easily propagate it to grow your collection or share with friends. Propagation is a simple process and can be done in a few easy steps:
- Identify the Pups: Aloe vera plants often produce "pups" or offsets, which are small clones of the parent plant. Wait until these pups are a few inches tall and have their own root systems.
- Separate the Pups: Gently remove the plant from its pot and locate the pups. Use a clean knife to cut them away from the parent plant, ensuring each pup has some roots attached.
- Let Them Callous: Allow the cut ends of the pups to dry and callous over for a day or two. This helps prevent rot when they're planted.
- Plant the Pups: Place each pup in its own pot with fresh succulent soil. Water lightly and place them in a location with bright, indirect light.
With a little patience, you'll see your new aloe vera plants taking root and growing strong. It's a wonderful way to expand your collection or gift a piece of your plant to someone special.
Using Aloe Vera Gel
Beyond its decorative value, aloe vera gel is a natural remedy that can be used for a variety of purposes. If you're interested in harvesting the gel from your plant, here's how you can do it:
- Select a Leaf: Choose a mature leaf from the outer section of the plant. These leaves will have the most gel.
- Cut the Leaf: Use a sharp knife to cut the leaf close to the base. Be careful not to damage the other leaves.
- Drain the Resin: Hold the cut leaf upright to allow the yellow resin (aloin) to drain out. This substance can be irritating to the skin, so it's best to let it drain for about 10-15 minutes.
- Extract the Gel: Lay the leaf flat and use a knife to remove the serrated edges. Slice the leaf open and scoop out the gel using a spoon.
Once extracted, you can store the gel in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to a week. Use it as a soothing treatment for minor burns, insect bites, or as a natural moisturizer. It's a handy remedy to have on hand, especially in the summer months!
Designing with Aloe Vera
Incorporating aloe vera into your home design can add a touch of greenery and elegance. Its unique form and texture make it a versatile choice for different spaces. Here are some ideas for styling aloe vera in your home:
- Minimalist Decor: Aloe vera's clean lines and sculptural shape fit perfectly in a minimalist setting. Place it in a sleek planter on a windowsill or a side table for a subtle pop of green.
- Bathroom Oasis: The bathroom is a great spot for aloe vera, as it thrives in humidity. Its soothing properties make it a fitting addition to your self-care routine.
- Desk Companion: Keep an aloe vera plant on your work desk to bring a bit of nature to your workspace. It's a low-maintenance plant that can brighten up your day.
- Grouping with Other Succulents: Aloe vera pairs well with other succulents. Create a beautiful arrangement by mixing it with different shapes and sizes to add variety and interest.
By thinking creatively, you can find the perfect spot for your aloe vera plant and enjoy its beauty in any room. It's all about making your space feel welcoming and lively.
Benefits of Aloe Vera Beyond Decoration
Aloe vera is more than just a pretty plant. Its health and wellness benefits are well-documented and make it a valuable addition to any home. Here are some ways aloe vera can be beneficial beyond its decorative appeal:
- Skin Care: Aloe vera gel is a popular ingredient in skincare products due to its moisturizing and soothing properties. It's often used to treat sunburns, acne, and dry skin.
- Digestive Health: Some people use aloe vera juice as a natural remedy for digestive issues. It can help soothe the digestive tract and promote regularity, although it's important to consult a healthcare professional before using it for this purpose.
- Air Purification: Like many houseplants, aloe vera can help improve indoor air quality by removing toxins such as formaldehyde and benzene from the air.
These benefits make aloe vera a multifunctional plant, offering both aesthetic and practical use. It's a small yet impactful addition to any home.
Choosing the Right Aloe Vera Plant
When it comes to choosing the right aloe vera plant for your home, there are a few things to consider. Here are some tips to help you select a healthy plant:
- Inspect the Leaves: Look for leaves that are firm and plump. Avoid plants with discolored or mushy leaves, as these may indicate poor health or disease.
- Check the Roots: If possible, gently remove the plant from its pot to inspect the roots. Healthy roots should be white and firm, not brown or mushy.
- Size and Space: Consider the size of the plant and the space you have available at home. While aloe vera plants are generally compact, some can grow quite large over time.
By paying attention to these details, you can ensure that you're bringing home a healthy, vibrant aloe vera plant that will thrive in your care.
Final Thoughts
We've covered a lot about aloe vera, from its history and benefits to practical care tips and creative ways to incorporate it into your home. This remarkable plant is not just a decorative piece but a symbol of nature's ability to nurture and heal.
At Cafe Planta, we love sharing our passion for plants with you. Whether you're looking for a stunning new addition or need advice on plant care, we're here to help. Feel free to email us or reach out on Instagram. Let's grow together and create a beautiful, thriving plant collection in your home.