Aloe vera is a plant with a reputation that precedes it. Known for its soothing gel, this succulent is a favorite not just for those with a green thumb, but for anyone who’s ever suffered a sunburn. But like any plant, aloe vera has its own set of preferences, especially when it comes to temperature. Ensuring your aloe is in the right climate can spell the difference between a thriving plant and a wilting one.
In this article, we'll chat about the temperature range that aloe vera loves, why this matters, and how you can create the perfect environment for your leafy friend. We’ll also touch on some other factors that pair with temperature, like humidity and light. Let’s jump in!
Understanding Aloe Vera’s Natural Habitat
Before diving into the specifics of temperature, it’s helpful to know where aloe vera comes from. Originating from the Arabian Peninsula, this plant has spread to various parts of the world, thriving in tropical and subtropical climates. This gives us a clue about its comfort zone in terms of temperature.
In its natural habitat, aloe vera is accustomed to warm temperatures and lots of sunlight. The plant’s thick, fleshy leaves are designed to store water, making it well-suited for dry, arid conditions. This means that while aloe vera can handle some temperature fluctuations, it prefers the warmer side of the spectrum.
Understanding this background helps us appreciate why temperature control is crucial. When temperatures drop, aloe vera’s growth slows, and it becomes susceptible to damage. Think of it as wearing a light jacket in winter—it's not exactly comfortable!
Ideal Temperature Range for Aloe Vera
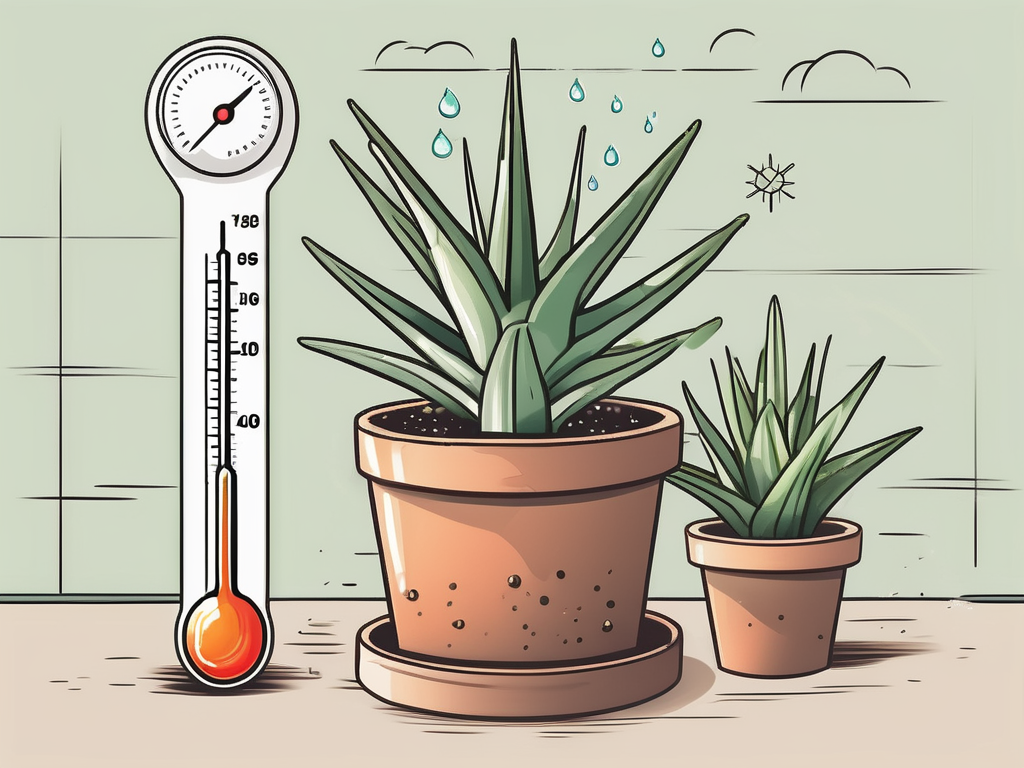
So, what’s the perfect temperature for your aloe vera? Generally, this plant thrives in temperatures ranging from 55°F to 80°F (13°C to 27°C). This range mimics the conditions of its native environment, providing warmth without too much heat.
During the day, aloe vera enjoys basking in temperatures between 70°F and 80°F (21°C to 27°C). This encourages active growth and allows the plant to photosynthesize efficiently. At night, the temperatures can safely dip to around 55°F to 60°F (13°C to 16°C). This drop is not only acceptable but natural, as many plants experience cooler nights in the wild.
It’s important to note that aloe vera can tolerate short periods of temperatures outside this range, but prolonged exposure to cold can lead to stress. If your home gets chilly at night, consider using a small space heater to maintain the warmth or relocate your plant to a cozier spot.
What Happens When Temperatures Drop?
When aloe vera is exposed to temperatures below its comfort zone, you might start to see some unhappy signs. Cold stress can manifest in several ways:
- Leaf Discoloration: The leaves may turn brown or black, indicating damage from the cold.
- Soft Spots: Cold temperatures can cause the leaves to develop mushy areas, a sign of cell damage.
- Stunted Growth: If it’s too cold, the plant might stop growing altogether.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s time to take action. Move your aloe vera to a warmer location and avoid watering it until it’s had a chance to recover. Cold-damaged leaves won’t heal, but the plant can still bounce back with the right care.
High Temperatures and Aloe Vera
On the flip side, what happens if things get too toasty? Aloe vera can handle high temperatures better than cold, thanks to its desert origins. However, excessive heat, especially if accompanied by direct sunlight, can still cause some issues.
When it gets too hot, you might see:
- Sunburn: Yes, even plants can get sunburned! You’ll notice bleached or scorched patches on the leaves.
- Dehydration: In extreme heat, the plant may lose moisture faster than it can absorb, leading to shriveled leaves.
To prevent heat stress, ensure your aloe vera has some protection from the midday sun, particularly if it’s near a window. A sheer curtain can diffuse harsh sunlight while still providing the light your plant loves.
Humidity Considerations
While temperature is crucial, humidity also plays a role in your aloe vera’s health. This plant prefers low humidity environments, similar to its native desert climate. High humidity can lead to problems like mold growth and root rot.
In most homes, humidity levels are just fine for aloe vera. However, if you live in a particularly humid area, consider these tips:
- Air Circulation: Use a fan to increase airflow around your plant, reducing humidity buildup.
- Dehumidifiers: These can help control moisture levels in the air, keeping your aloe vera happy.
Remember, it’s all about balance. While aloe vera can handle dry conditions well, it still needs occasional watering to stay hydrated. Just be cautious not to overdo it, leading to soggy soil.
Seasonal Changes and Aloe Vera Care
As seasons change, so should your care routine for aloe vera. During the warmer months, your plant will likely be in a growth phase, enjoying the increase in daylight and warmth. This is the time to water and feed more regularly.
In the cooler months, especially if temperatures drop significantly, your aloe vera will enter a dormancy period. Reduce watering, as the plant will use less water during this time. It’s also a good idea to keep the plant away from drafty windows or doors where cold air might seep in.
Adjusting your care routine with the seasons ensures that your aloe vera remains healthy throughout the year, adapting naturally to its environment.
Creating the Perfect Spot Indoors
Finding the right spot for your aloe vera inside your home can make all the difference. While the plant is quite forgiving, placing it in an ideal location helps it thrive with minimal effort.
Here’s what to look for:
- Light: A south or west-facing window is usually ideal, providing bright, indirect sunlight.
- Away from Drafts: Keep your plant away from air vents or frequently opened windows and doors.
- Stable Temperatures: Avoid areas that experience significant temperature fluctuations, like near ovens or fireplaces.
By finding the right spot, you’re setting your aloe vera up for success, giving it the conditions it needs to flourish.
Temperature Tools and Gadgets
In today’s world, we have plenty of tools at our disposal to help monitor and maintain the perfect environment for our plants. For those who love a little tech, consider these gadgets:
- Thermometers: Digital thermometers can help you keep an eye on the temperature around your aloe vera, ensuring it stays within the ideal range.
- Smart Plugs: Use these to automate fans or heaters, maintaining a consistent environment without manual intervention.
- Humidity Meters: These devices give you a quick read on the humidity levels, ensuring they’re not too high or too low.
While these tools aren’t necessary, they can be fun and helpful additions for any plant lover looking to optimize their indoor garden.
Final Thoughts
Temperature plays a crucial role in the health and happiness of your aloe vera. By understanding its needs and adjusting your care routine accordingly, you can ensure your plant stays vibrant and robust all year round.
Here at Cafe Planta, we're all about helping you nurture your plant collection. Whether you're looking for a new addition or need advice on plant care, we're here to support you. Feel free to email us or reach out via our Instagram. Let's grow together and create spaces that connect us with nature.